Execution of SELECT Statement in Oracle
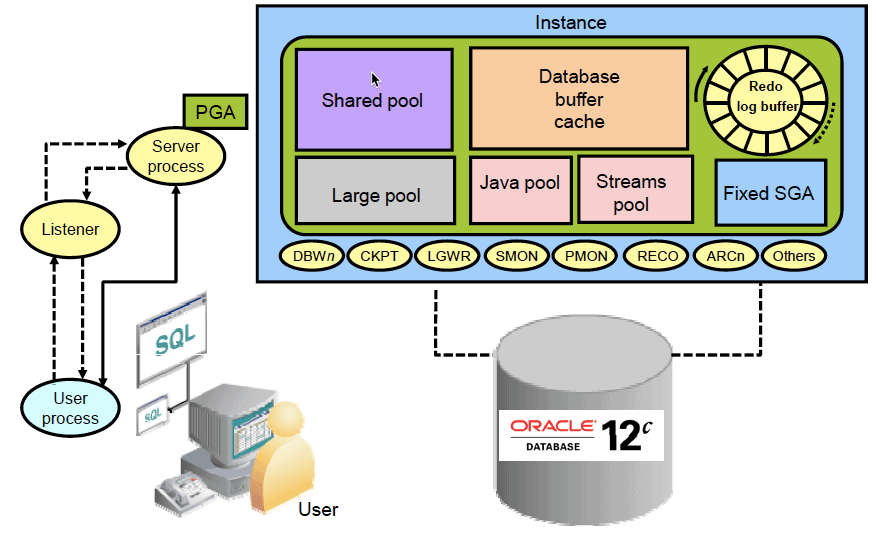
Overview of Oracle Database Architecture 12c before discussion about execution of SQL statement
Shared Pool :
- Library Cache : Executable Code of SQL / PLSQL
- Data Dictionary Cache: System Metadata
DB Buffer Cache : It Contains data pieces read from Datafiles
Redo Log Buffer : Data Changes are recorded in the redo log buffer.
( Parse / Execute / Fetch)

t is done in the following steps:
- Step-1:
Parser: During parse call, the database performs the following checks- Syntax check, Semantic check and Shared pool check, after converting the query into relational algebra.Parser performs the following checks as (refer detailed diagram):- Syntax check – concludes SQL syntactic validity. Example:
SELECT * FORM employee
Here error of wrong spelling of FROM is given by this check. - Semantic check – determines whether the statement is meaningful or not. Example: query contains a tablename which does not exist is checked by this check.
- Shared Pool check – Every query possess a hash code during its execution. So, this check determines existence of written hash code in shared pool if code exists in shared pool then database will not take additional steps for optimization and execution.
Hard Parse and Soft Parse – - Syntax check – concludes SQL syntactic validity. Example:
- If there is a fresh query and its hash code does not exist in shared pool then that query has to pass through from the additional steps known as hard parsing otherwise if hash code exists then query does not passes through additional steps. It just passes directly to execution engine (refer detailed diagram). This is known as soft parsing.
- Hard Parse includes following steps – Optimizer and Row source generation.
Step-2:
Optimizer: During optimization stage, database must perform a hard parse atleast for one unique DML statement and perform optimization during this parse. This database never optimizes DDL unless it includes a DML component such as subquery that require optimization.
It is a process in which multiple query execution plan for satisfying a query are examined and most efficient query plan is satisfied for execution.
Database catalog stores the execution plans and then optimizer passes the lowest cost plan for execution.
Database catalog stores the execution plans and then optimizer passes the lowest cost plan for execution.
- Row Source Generation –
The Row Source Generation is a software that receives a optimal execution plan from the optimizer and produces an iterative execution plan that is usable by the rest of the database. the iterative plan is the binary program that when executes by the sql engine produces the result set. - Step-3:
Execution Engine: Finally runs the query and display the required result.
Comments
Post a Comment