Oracle 12c – Multitenant Architecture & Creating database manually
Containers in Multitenancy
Oracle Database 12c introduced a new feature called “multitenant.” The multitenant feature provides the ability for a single instance to manage multiple databases. The multitenant architecture enables an Oracle database to function as a multitenant container database (CDB).
The multitenant architecture comprises the following :
“Multitenant” Database Instance:
This is a term used to distinguish between a database instance that supports multitenant database and one that does not.
Container Database (CDB):
This is the database that is created when that database supports Oracle’s multitenant option. It’s also called the ROOT container and is the CDB$ROOT within the data dictionary views of the CDB.
Root Container Database: This is created automatically when you create a multitenant database. The root container contains the data dictionary for the CDB.
Pluggable Database (PDB): These are the databases that are stored within the CDB. A PDB is a portable collection of schemas, schema objects, and non schema objects that appears to an Oracle Net client as a non-CDB.
Note :
A Container Database (CDB) comprises zero, one, or many customer-created pluggable databases. All Oracle databases before Oracle Database 12c were non-CDBs.
A Container Database (CDB) comprises zero, one, or many customer-created pluggable databases. All Oracle databases before Oracle Database 12c were non-CDBs.
Oracle Multitenant offers the ability to have up to 252 PDBs per multitenant container database. The multitenant architecture with one user-created pluggable database (single tenant) is available in all editions without the multitenant option.
Database Environment Before Database Consolidation
Single Container Database
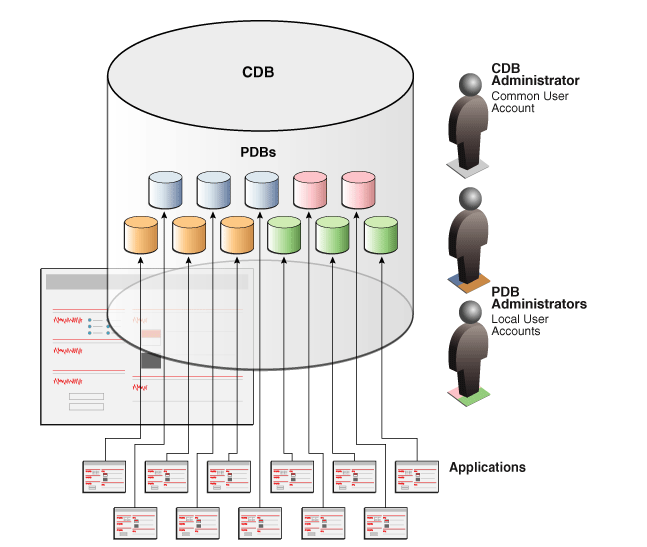
Container DB with Seed & PDB’s
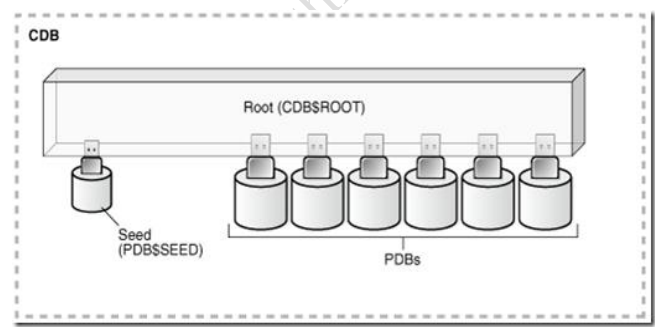
The ROOT
The root container, also called the root, is a collection of schemas, schema objects, and nonschema objects to which all PDBs belong. Every CDB has one and only one root container, which stores the system metadata required to manage PDBs. All PDBs belong to the root.
The name of the root is CDB$ROOT.
The root does not store user data. Thus, you must not add user data to the root or modify system supplied schemas in the root.
However, you can create common users and roles for database administratio.
A common user with the necessary privileges can switch between PDBs.
The SEED
The seed PDB is a system-supplied template that the CDB can use to create new PDBs.
The seed PDB is named PDB$SEED.
You can add or modify objects in PDB$SEED.
Pluggable Database
A Pluggable database (PDB) is a user-created entity that contains the data and code required for a specific set of features.
For example, a PDB can support a specific application, such as a human resources or sales application.
No PDBs exist at creation of the CDB. You add PDBs based on your requirement.
Currently Oracle 12c supports up to 252 Pluggable Databases in a single container.
Data Objects in a CDB
A container data object is a table or view containing data pertaining to multiple containers and possibly the CDB as a whole, along with mechanisms to restrict data visible to specific common users through such objects to one or more containers.
Examples of container data objects are Oracle-supplied views whose names begin with V$ and CDB_.
All container data objects have a CON_ID column shows the meaning of the values for this column.

How to create/set up container database
There are three ways to create container database, as follows:
- Database Configuration Assistant (DBCA)
- Oracle Universal Installer (OUI)
- Manual Creation
Manual Creation:
Steps for creating container database :
- Set environmental variable by using .bash_profile
- Create parameter file (pfile).
- Create directory structure.
- Keep the database in nomount state.
- Create database creation script and run at SQL prompt.
- Post database creation steps: -Run the required scripts at SQL prompt.
Prerequisites for creating database:
- Sufficient primary memory should be available to start the Oracle instance.
- Sufficient disk space must be available on the computer.
Step 1: setting environment variable with .bash_profile
Step 2: create parameter file (pfile)
Step 3: create directory structure
Step 4: Connect to SQL* PLUS and keep the database in nomount state.
Step 5: Create database creation script .
Run at SQL prompt.
Step 6 : Run the database scripts to create the required views and tables in the database.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
SYS> conn system/manager
SYS>@$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/catalog.sql
SYS>@$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/catblock.sql
SYS>@$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/catproc.sql
SYS>@$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/catoctk.sql
SYS>@$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/owminst.plb
SYS>@$ORACLE_HOME/sqlplus/admin/pupbld.sql
|
Comments
Post a Comment