Tablespace Management In Oracle
Tablespace Management in Oracle.


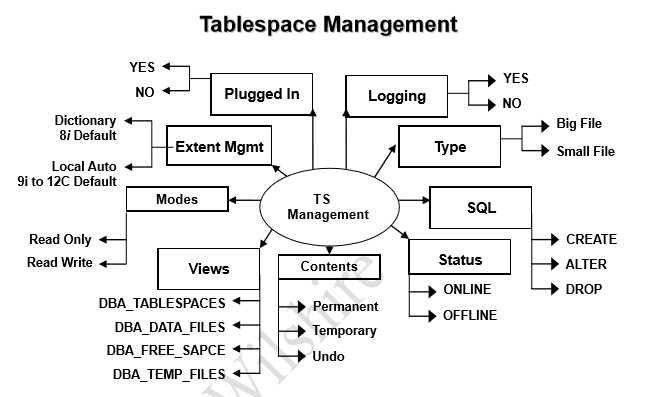
Following Topics are covered :
- Create Tablespace with an Example
- Create Tablespace with Additional Storage Parameters
- Add New Datafile to Increase the Size of a Tablespace
- Add New Datafile with Storage Parameters
- How to Increase Size of an Existing Datafile
- View Tablespace and datafile Information
- Tablespace Extent Management
- Calculate the Size of your Tablespace (Both Total Space and Free Space Available)
- Bigfile Tablespace Management
- Rename Tablespace
- Drop Tablespace
- Drop a Specific datafaile from a Tablespace
- Bring Tablespace Online or Offline
- Set a Tablespace as Read-Only Temporarily
- Rename or Move Datafile to a Different Folder
What is a tablespace and datafile:
Tablespace is the primary logic structure of the oracle database. It consists of one or more physical datafiles. Datafiles physical stores database data in storage.(DISKS) . So when we create a datafile of 30G in database, it will eat 30G of space from defined storage. All the table or index segment is created in tablespace only.
Types of Tablespace:
SYSTEM TABLESPACE:
- Each database contains a SYSTEM tablespace.( It is created by default while creating the database itself) .
- It contains the data dictionary tables of the database.
- All the view,procedures, functions, packages and triggers are stored in SYSTEM tablespace
- It is not recommended to user SYSTEM tablespace for creating any other table or index.
SYSAUX TABLESPACE:
- All the database metadata, that doesnt store in SYSTEM tablespace, will be stored here.
- Many database components datas are stored in this tablespace
PERMANENT TABLESPACE:
- When someone says tablespace, Means they are mostly refering to PERMANENT TABLESPACE
- This tablespace are used for storing the actual schema tables or indexes . i.e it Stores user data.
- It doesnt store any of the data dictionary tables.
There are two types of PERMANENT TABLESPACE.
- SMALL FILE – (DEFAULT) – This is the common size tablespace, It can contain multiple datafiles with each datafile of size 31G;
- BIG FILE – It can contain only one datafile which can grow upto 128 TB.
UNDO TABLESPACE:
- This tablespace stores Undo data:
- We can’t create any table or index inside undo tablespace.
- Each instance in the database have one defined UNDO tablespace. i.e for standalone database one assigned undo tablespace, and for multi node rac system, each instance on the node will have one assigned undo tablespace.
TEMPORARY TABLESPACE:
- This tablespace stores the data temporarily for sessions doing sorting and join operations.
- Sort operations are also generated by SELECT * FROM WHERE CLAUSE that join rows from within tables and between tables. The segments generated during this process will be stored in temp tablespace.
- Each database will have one default temporary tablespace.
TABLESPACE DDL
--------------
set pagesize 0
SET LONG 9999999
select dbms_metadata.get_ddl('TABLESPACE','&TABLESPACE_NAME') FROM DUAL;
Tablespace Utilization Script :
Tablespace Utilization Script :
SELECT /* + RULE */
df.tablespace_name "Tablespace",
df.bytes / (1024 * 1024) "Size (MB)",
SUM(fs.bytes) / (1024 * 1024) "Free (MB)",
Nvl(Round(SUM(fs.bytes) * 100 / df.bytes), 1) "% Free",
Round((df.bytes - SUM(fs.bytes)) * 100 / df.bytes) "% Used"
FROM dba_free_space fs,
(SELECT tablespace_name, SUM(bytes) bytes
FROM dba_data_files
GROUP BY tablespace_name) df
WHERE fs.tablespace_name(+) = df.tablespace_name
GROUP BY df.tablespace_name, df.bytes
UNION ALL
SELECT /* + RULE */
df.tablespace_name tspace,
fs.bytes / (1024 * 1024),
SUM(df.bytes_free) / (1024 * 1024),
Nvl(Round((SUM(fs.bytes) - df.bytes_used) * 100 / fs.bytes), 1),
Round((SUM(fs.bytes) - df.bytes_free) * 100 / fs.bytes)
FROM dba_temp_files fs,
(SELECT tablespace_name, bytes_free, bytes_used
FROM v$temp_space_header
GROUP BY tablespace_name, bytes_free, bytes_used) df
WHERE fs.tablespace_name(+) = df.tablespace_name
GROUP BY df.tablespace_name, fs.bytes, df.bytes_free, df.bytes_used
ORDER BY 5 DESC;
df.bytes / (1024 * 1024) "Size (MB)",
SUM(fs.bytes) / (1024 * 1024) "Free (MB)",
Nvl(Round(SUM(fs.bytes) * 100 / df.bytes), 1) "% Free",
Round((df.bytes - SUM(fs.bytes)) * 100 / df.bytes) "% Used"
FROM dba_free_space fs,
(SELECT tablespace_name, SUM(bytes) bytes
FROM dba_data_files
GROUP BY tablespace_name) df
WHERE fs.tablespace_name(+) = df.tablespace_name
GROUP BY df.tablespace_name, df.bytes
UNION ALL
SELECT /* + RULE */
df.tablespace_name tspace,
fs.bytes / (1024 * 1024),
SUM(df.bytes_free) / (1024 * 1024),
Nvl(Round((SUM(fs.bytes) - df.bytes_used) * 100 / fs.bytes), 1),
Round((SUM(fs.bytes) - df.bytes_free) * 100 / fs.bytes)
FROM dba_temp_files fs,
(SELECT tablespace_name, bytes_free, bytes_used
FROM v$temp_space_header
GROUP BY tablespace_name, bytes_free, bytes_used) df
WHERE fs.tablespace_name(+) = df.tablespace_name
GROUP BY df.tablespace_name, fs.bytes, df.bytes_free, df.bytes_used
ORDER BY 5 DESC;
Published query of tablespace Utilization are tested in Test environments
ReplyDelete